Urban development authorities play a pivotal role in shaping the infrastructure and growth of cities. In this blog, we will compare the Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority (AUDA), Gandhinagar Urban Development Authority (GUDA), Vadodara Urban Development Authority (VUDA), and Surat Urban Development Authority (SUDA). This comparison will help us understand their roles, responsibilities, governance structures, and notable projects.
Getting to Know AUDA, GUDA, VUDA, and SUDA: Who Are They?
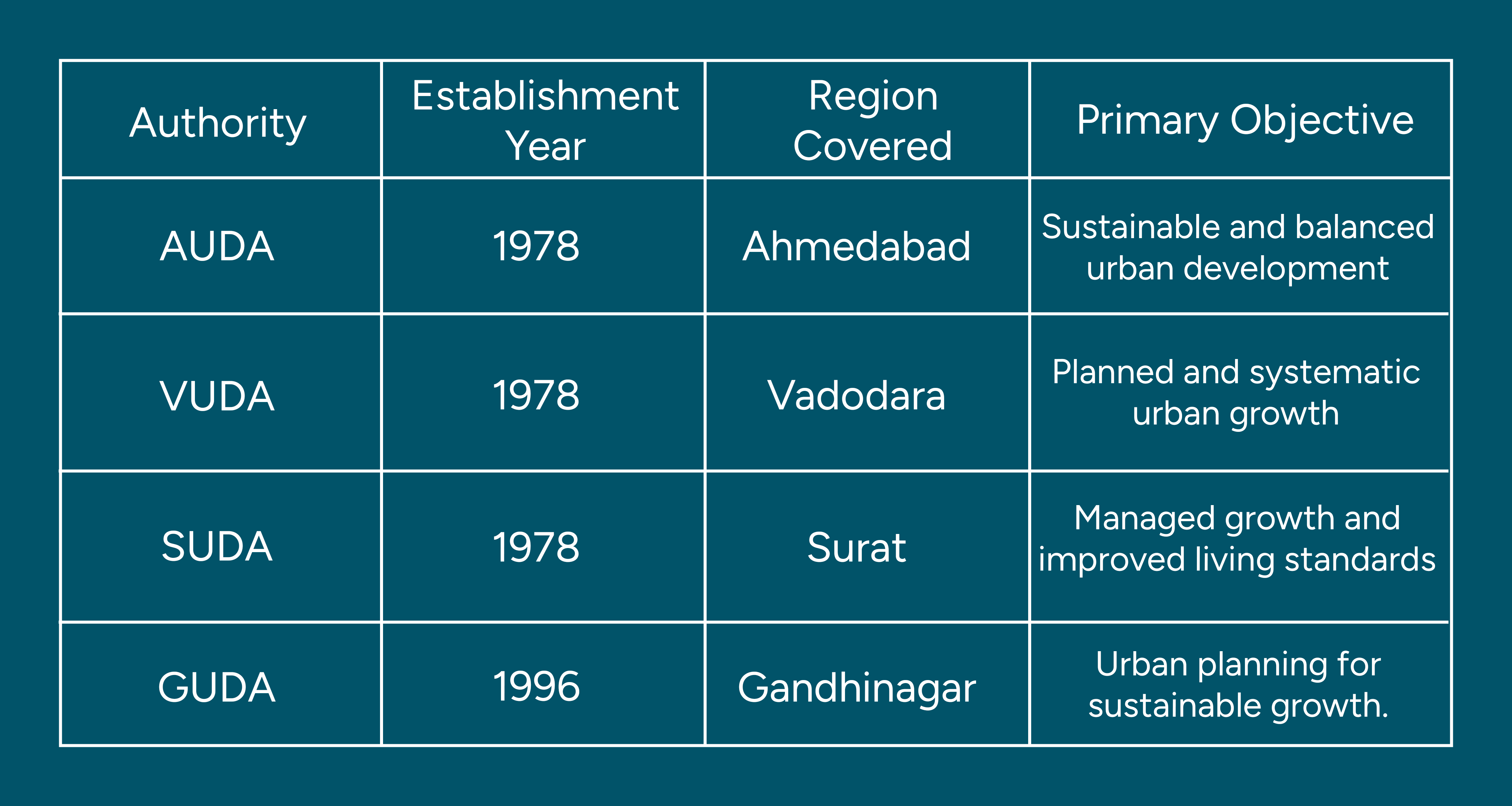
Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority (AUDA):
Formed to look into the planning and development of the city of Ahmedabad.
Function according to the Gujarat Town Planning and Urban Development Act, 1976.
Concerned with the administration of cities, construction of structures and physical facilities, and attaining long-term growth.
Gandhinagar Urban Development Authority (GUDA):
Formed to control the organized development of Gandhinagar.
Involved in the construction of structures, proper utilization, and enhancement of the surrounding environment and facilities.
Strives to retain the status of the capital city of Gujarat.
Vadodara Urban Development Authority (VUDA):
Responsible for planning, coordinating and supervising the development of Vadodara and the regions in and around it.
Concentrates on the construction of infrastructure and houses and environmental preservation.
The Gujarat state government provides supervision to function as a regulating authority.
Surat Urban Development Authority (SUDA):
It is an organization that was founded in 1978 to cater to the development management of the Surat Metropolitan Region.
Controls the land use planning, zoning, and physical infrastructure of cities.
This guarantees the generation of sustainable revenues for the growth of the community while at the same time improving the standards of living of the people.
Responsibilities and Functions:
AUDA:
Supervises the making of cities regarding architectural and other structures and the creation of changes in the environment.
Emphasizes adequate housing for everyone and the ability to build structures that will be environmentally friendly in the future.
It guarantees the execution of development programs, for instance, the construction of transport networks and systems of disposal.
GUDA:
Construction of various infrastructures such as roads, provision of water, and proper disposal of wastes.
Designing the areas of living and business.
Preservation and protection of the environment, as well as ensuring that urban development is sustainable.
VUDA:
Coordinates the development and expansion of Vadodara and its environs.
Arose within the context of the reasonable and efficient use of space, construction of facilities, and environmental management.
Being associated with slum development, construction of houses, and other public facilities.
SUDA:
Regulates development in the Surat Metropolitan Area.
Disseminates land use plans or layouts and urban development plans and also prepares and mounts these.
Produces employment chances and helps in the preservation of the surroundings.
Key Projects:
AUDA:
Sabarmati Riverfront Development: Used the recreational aspect of the river and changed the banks from simple river banks to cultural arenas.
Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS): Better and more efficient public transport system and less crowd on the roads.
Smart City Project: Concentrating on traffic flow, management of wastes, and decrease of crime rates.
GUDA:
GIFT City: A major financial and IT services hub.
Enhancement of urban amenities and infrastructure projects.
VUDA:
Ajwa Water Supply Scheme: Adopts a routine of water supply to Vadodara city.
Central Bus Terminal: Improved transportation accessibility and community relations.
River Vishwamitri Development: Concerns to flood management and the aesthetic improvement of river banks.
SUDA:
Tapi Riverfront Development: Implemented environment-friendly urban areas and enhanced waste collection.
Surat Diamond Bourse: Contributed to the growth of trade and the economy of Surat.
Surat Metro Rail: Improves city accessibility and traffic organization.
Where Do They Operate? Understanding Their Geographic Reach
AUDA:
Operates in Ahmedabad and its surrounding towns and villages.
Active in municipal and urban areas, focusing on construction and urbanization.
GUDA:
Covers Gandhinagar city and surrounding areas.
Engages in developing key infrastructure and urban amenities.
VUDA:
Manages the urban development of Vadodara and its nearby regions.
Engaged in the creation of new residential areas and increased accessibility.
SUDA:
Oversees the Surat Metropolitan Region.
Manages construction and growth in the city of Surat as well as the rural areas.
How Are They Run? A Look at Their Governance Structures
AUDA:
Governed by the Gujarat Town Planning and Urban Development Act.
Works in coordination with the Gujarat state government.
GUDA:
Operates under the state government’s guidance.
Ensures sustainable development through coordinated planning.
VUDA:
Governed by a board of directors, which is nominated by the state government.
Focuses on strategic planning and implementation of development projects.
SUDA:
Governed by the Gujarat Town Planning and Urban Development Act.
Collaborates with local governments and stakeholders for balanced development.
Looking Ahead: Future Plans and Visions for Urban Development
AUDA:
Metro Rail System Expansion: Greater efforts to reduce traffic jams and improve connectivity.
Green Urban Spaces: Developing urban green spaces and beautification projects.
Smart City Technologies: Implementing advanced technologies for optimizing services.
GUDA:
GIFT City Development: Further development for better facilities and infrastructure.
Sustainable Growth: Enhancing infrastructure and urban amenities to support growth.
VUDA:
Public Transport Improvement: Focus on improving public transport and creating green areas.
Sustainable Development: Promoting environmental conservation and sustainable urban growth.
SUDA:
Sustainable Development: Attempts to improve the process of sustainable development and the construction of city facilities.
Economic Development: Promoting economic development and community initiatives.
Conclusion:
Thus, AUDA, GUDA, VUDA, and SUDA are significant for the development of their cities since they are the urban development authorities. However, each authority has its objectives of achieving sustainable and economic growth and enhancing the standards of living of the people, but all of them formulate their policies according to the nature of problems and potentials of their respective domains. Many of these authorities are involved in the strategic and constant planning and development of Ahmedabad, Gandhinagar, Vadodara, and Surat so that these cities become progressive, integrated, and adequately equipped places.